How long can a dog go without food? According to the American Kennel Club, a healthy dog can fast for up to two weeks without any ill effects. However, if your dog is younger, pregnant, or nursing, she will need to eat more frequently. And of course, if your dog is showing signs of weakness or hunger, it’s time to break the fast.
Introduction
A dog may be able to go without food for a period of time, but water is essential for their survival. Depending on a number of factors, such as age, weight, health, and activity level, a dog can live without food for anywhere from a few days to several weeks. However, without water, they will only survive for a matter of days.
It’s important to keep in mind that going without food or water will cause your dog severe distress and can lead to organ damage or failure.
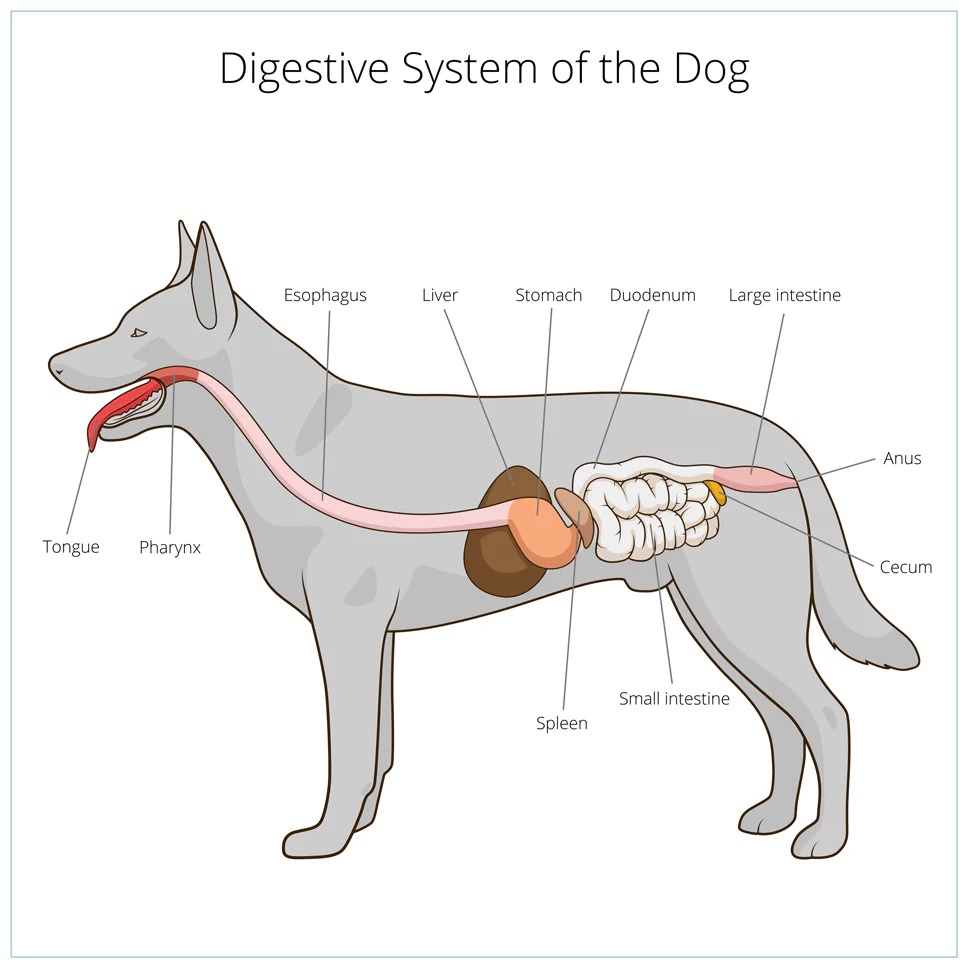
The Dog’s Digestive System
Most dogs will have no problem going for a day or two without food, especially if they have enough water to drink. The length of time a dog can go without food depends on a number of factors, including their age, health, and activity level. Keep reading to learn more about how long dogs can go without food and what factors affect their digestion.
The Stomach
The stomach is a muscular sac about the size of a small melon that expands when filled with food. The stomach’s main job is to begin breaking down the food we eat.
Despite popular belief, the stomach is not where digestion and nutrient absorption primarily take place. In fact, digestion and nutrient absorption primarily take place in the small intestine.
The stomach does have an important role in digestion, though. The stomach produces strong acids and enzymes that continue to break down food. These digestive juices also kill bacteria that might be present in food.
The stomach muscles push food and liquid into the small intestine through a muscle called the pylorus. The pylorus is a one-way valve, so once food enters the small intestine it cannot return to the stomach.
The Small Intestine
The small intestine is about 20 feet long in a dog and is where most of the nutrients from food are absorbed. The small intestine is divided into three sections, the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Bile from the gallbladder and enzymes from the pancreas are released into the small intestine to help with digestion.
The walls of the small intestine have millions of tiny, fingerlike projections called villi. The villi increase the surface area of the intestine so that more nutrients can be absorbed.
The ileum is the last section of the small intestine and opens into the large intestine at a place called the ileocecal valve.
The Large Intestine
The large intestine is about 1.5 metres long and leads from the caecum to the rectum. Its main function is to absorb water from the chyme (the partially digested food that leaves the small intestine), which forms faeces.
The large intestine is much wider than the small intestine (about 10cm in diameter) and has a different type of lining, which is why it can absorb water so effectively. The faeces leave the large intestine and pass into the rectum, where they are stored until they are passed out of the body through the anus.
Factors Affecting How Long a Dog Can Go Without Eating
A dog’s health, age, activity level, and breed all play a role in how long he can go without food. A young, healthy dog with no health problems can usually go longer without food than an older dog or a dog with health issues.
Age
A young, healthy puppy can usually go without food for a day or so without any ill effects, while an older dog may only be able to hold out for a few hours. If your dog is very old or sick, he may not be able to go more than a few hours without food.
Size
Size is probably the most important factor in how long a dog can go without eating. In general, the larger the breed of dog, the longer it can go without food.
Breed
Small breeds have fast metabolisms and need to eat more frequently than large breeds. Large breeds can go longer between meals, but they still need to eat at least once a day. toy and miniature breeds, on the other hand, may need to eat two or three times a day.
Activity Level
One of the biggest factors that will affect how long your dog can go without eating is their activity level. A dog who is very active, either because they have a high energy level or because they are working dogs, will need to eat more often than a dog who is less active.
Active dogs need to eat more often because they are burning more calories and they need to replenish those calories on a regular basis. If you have an active dog, you should be feeding them at least twice a day, and possibly more if they are working dogs.
In contrast, a less active dog can usually go a little longer between meals and may only need to be fed once or twice a day. However, even less active dogs should not go more than 24 hours without eating, so if your dog does not want to eat for that long, it is important to take them to the vet to find out if there is an underlying health issue.
Health Conditions
Health conditions are one of the main factors that will affect how long a dog can go without eating. Dogs that are suffering from illnesses or have just undergone surgery will have a decreased appetite and may not feel like eating for days at a time. If your dog is unwell, it’s important to take him to the vet so that he can be checked out and given any necessary treatment.
Other factors that can affect a dog’s appetite include:
-Pain – if your dog is in pain, he may not want to eat.
-Stress – dogs that are stressed (for example, because they’ve just moved house or been left alone for long periods of time) may also lose their appetite.
When to Be Concerned
If your dog goes more than two days without eating, this is cause for concern and you should take him to the vet. If he’s only missed one meal, however, there’s no need to worry.
How to Prevent Your Dog From Going Too Long Without Eating
Most dogs will not go more than three days without eating, however, some may go as long as seven days. If you are concerned that your dog has not eaten in a while, there are some things you can do to help.
Feeding Schedules
When it comes to how often to feed your dog, there is no one answer that fits all dogs. The frequency of meals will depend on a number of factors, including your dog’s age, activity level, and general health.
Puppies and young dogs, for example, will need to eat more often than adult dogs because their bodies are growing and developing at a rapid pace. Senior dogs, on the other hand, may do better on two smaller meals per day instead of one large one.
As a general rule of thumb, most healthy adult dogs can go about four to six hours between meals without any problems. If you are feeding your dog twice per day, this means that each meal should be spaced about four to six hours apart.
Of course, there will always be exceptions to this rule – some dogs may do fine on three smaller meals per day while others may need to eat every few hours to avoid getting too hungry. It is best to talk with your veterinarian about what feeding schedule is best for your individual dog.
Proper Nutrition
Many factors can contribute to how often you should feed your dog, such as their age, activity level, and health condition. However, as a general rule of thumb, dogs should be fed at least once a day.
Some dogs may need to be fed more frequently, especially young puppies or older dogs with poor appetites. If you’re unsure how often to feed your dog, talk to your veterinarian for specific recommendations.
Avoiding Food Aversions
- Make sure your dog is getting enough exercise. A tired dog is more likely to be interested in food.
- Feed your dog several times a day, instead of just once or twice. This will help keep his appetite steady.
- Don’t make a big deal out of mealtimes. If your dog sees you getting excited about food, he may start to get anxious and lose his appetite. -Try different types of food and flavors to find something your dog likes. Dogs can be picky eaters, so it may take some trial and error.
- Talk to your veterinarian if you’re concerned about your dog’s appetite. He may be able to recommend a food that’s more appetizing or suggest a medical problem that’s causing the issue.
Managing Stress
One of the best ways to prevent your dog from going too long without eating is to manage their stress levels. Dogs can become stressed for a number of reasons, including changes in their routine, overwhelming situations, boredom, and more. When dogs are stressed, they may not have an appetite and may go long periods of time without eating.
There are a number of ways you can help your dog manage their stress levels.
First, make sure their environment is as calm and relaxed as possible. If they’re used to a lot of activity, try to reduce it gradually so they don’t get overwhelmed.
Secondly, provide them with plenty of opportunities to exercise and burn off energy – this will help them stay calm and relaxed. Finally, make sure they have plenty of mental stimulation – this can be provided through interactive toys, training sessions, and more. By managing your dog’s stress levels, you can help prevent them from going too long without eating.